My chosen approach to write about is Experimental Learning!
Overview
Experimental Learning is described as placing emphasis on hands-on, self-directed and experiential learning processes. Some key characteristics of this approach includes:
- Experiential Engagement: Engaging with the tools or technologies directly, actively participating in prototyping and testing. Learners digests new concepts by doing instead of memorization.
- Active Participation: Instead of following a series of defined steps, learners would actively devise solutions to problems or errors. And adapting based on feedback.
- Self-Direction and Agency: Learners take ownership of their work, leading to more intrinsic motivation for deeper understanding.
- Discovery-Driven Learning: Instead of memorizing, learners would discover insights throughout the solutioning process, by going through countless trials and errors.
Based on these definitions from the California Learning Resource Network (California Learning Resource Network. (n.d.)), I can provide some examples on Experimental Learning:
- Learning a new programming language through porting your previous work into that new language.
- Learning chemical formulas through conducting an experiment recreating that substance.
- Learning a new cooking technique through attempting to recreate a dish using said technique.
Alignment with topic
Our chosen topic for our group is “Teaching better AI usage for students through asking better prompts and exploration of different AI models”.
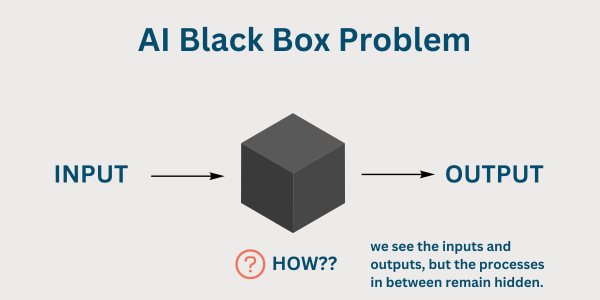
Figure 1: AI black box theory (Monga, A., 2024)
While AI theories exists, this only explains the the building process of an AI chat-bot and the algorithms behind it. This leads to the “black box” nature of deep learning algorithms, you can only see the input and output, not the inner workings. We want to take a continuous learning and improvement approach through practical examples and experimentation, since it is impossible to create concrete theory from a “black box”. This leads to Experimental Learning aligning perfectly with out topic.
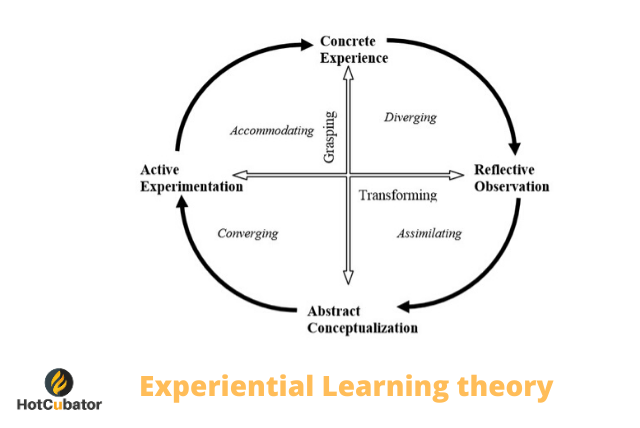
Figure 2: Kolb’s Experiential Learning Theory (Rahman, 2021)
An example approach that highlights this alignment is using Kolb’s Experiential Learning Theory (ELT). We can apply the framework Kolb created to our topic as following:
- Concrete experience: Showcasing a wrongful response to a vague prompt, creating emotional engagement.
- Reflective observation: Class discussions on why the prompt is vague causing wrongful response.
- Abstract conceptualization: Introducing common prompting practices and how it would alleviate some of the issues shown.
- Active experimentation: Let learners attempt to rewrite the previous prompt.
References
- California Learning Resource Network. (n.d.). What is experimental learning? Retrieved July 27, 2025, from https://www.clrn.org/what-is-experimental-learning/
- KOLB, D. A., BOYATZIS, R. E. & MAINEMELIS, C. 2001. Experiential learning theory: Previous research and new directions. Perspectives on thinking, learning, and cognitive styles, 1, 227-247.
- Monga, A. (2024, May 19). The AI black box: Why cybersecurity professionals should care. Medium. https://medium.com/@ajay.monga73/the-ai-black-box-why-cybersecurity-professionals-should-care-4bec7ff32c7c
- Rahman, M. (2021, November 28). Experiential learning theory: A practical approach to learning. HotCubator. https://hotcubator.com.au/higher-education/experiential-learning-theory-a-practical-approach-to-learning/
- Stelzner, E. (2024, March 18). What is black box AI? Built In. https://builtin.com/articles/black-box-ai
Leave a Reply to npham49 Cancel reply